

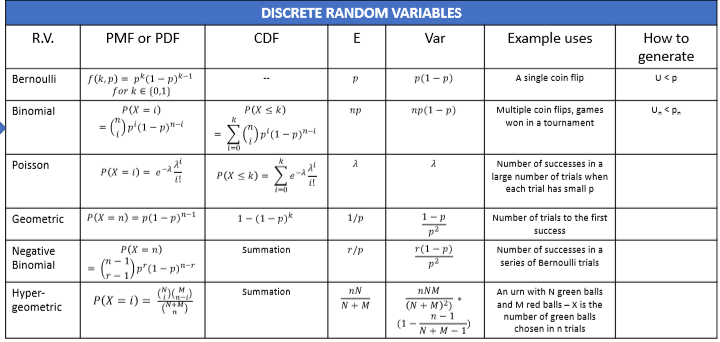
p(3 ≤ x ≤ 4).įigure 2: Normal distribution time spent on reading a blog page References The shaded area in Figure 2 represents the probability that the time spent on reading a blog page inīetween 3 to 4 minutes i.e. Let's take an example, a daily time spent on reading a blog page is approximately normally distributed with a mean of 3 The normal distribution, exponential distribution, and uniform distribution are continuous probability distributions.Values of X which are less than or equal to some value p(X ≤ x ). Similar to PDF, cumulative distribution function (CDF) is used for calculating the probability for all.That X takes any single value is always zero. Generally, the probability of interval is calculated in continuous probability distributions because the probability.The total area under the curve is always equal to one. The a and b is equal to the area under the curve of a and b. The probability p(a ≤ x ≤ b) of any value between

Interval between the two values (a and b) of X.
Random variable (countable quantity such as 0, 1, 2, and so on and not fractions, e.g. Discrete probability distributions explain the probabilities associated with each possible outcome of a.Depending on the type of random variable - discrete or continuous - probability distributions classified as discrete and continuous.Probability distributions represent the probabilities associated with all outcomes of a random variable.References What is Probability Distributions?.Probability mass function (PMF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF).Find probabilities using discrete and continuous probability distributions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
